Retinal Diseases
What is a retinal disease?
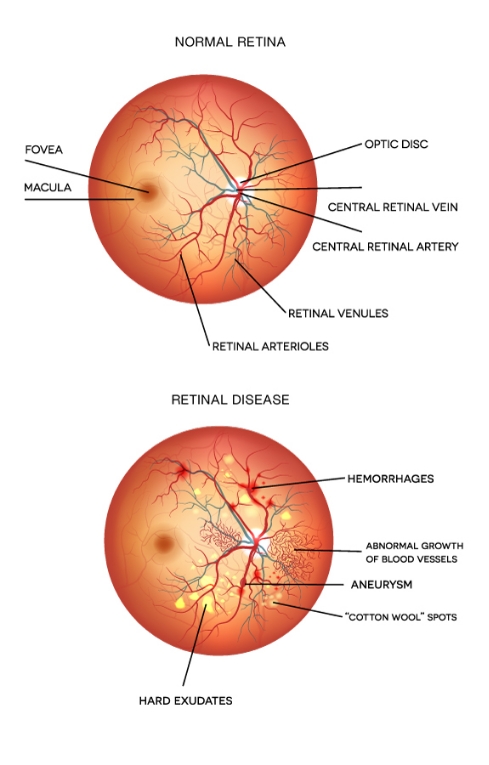
The retina is a thin, light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that is crucial for translating light into visual information. Retinal diseases can affect different parts of the retina, leading to impaired vision, discomfort, or severe complications.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to preserve vision and maintain quality of life.
When to seek consultation:
symptoms of retinal diseases
Recognizing the symptoms of retinal diseases is essential to seek prompt specialist care.
If these symptoms occur, scheduling an eye examination with a retina specialist can lead to early diagnosis and tailored treatment.
Protect your vision—book an appointment today
Common signs include but are not limited to:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Sudden flashes of light or floating spots in the visual field
- Gradual or sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Dark or empty areas in the visual field
- Difficulty seeing at night
Types of retinal diseases and their treatments
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive condition caused by damage to the retina’s blood vessels due to diabetes. It is a leading cause of vision loss among adults. All diabetics need yearly follow up at a minimum unless otherwise suggested by your doctor.
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through four stages:
1. Mild non-proliferative retinopathy
Early swelling in retinal blood vessels, often symptomless.
2. Moderate non-proliferative retinopathy
Blocked blood vessels leading to poor circulation in parts of the retina.
3. Severe non-proliferative retinopathy
Widespread blockage prompting the retina to grow abnormal vessels.
4. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
Fragile new blood vessels form, potentially causing bleeding and retinal detachment.
Diabetic macular edema (DME)
A major complication of diabetic retinopathy, DME occurs when fluid leaks into the macula—the part of the retina crucial for sharp central vision. It can arise at any stage of diabetic retinopathy and is the most common cause of vision loss in people living with diabetes.
Treatment options for diabetic retinopathy
Early-stage diabetic retinopathy may not require immediate treatment, but close monitoring and better management of diabetes are essential. As the condition advances, several treatment options can slow its progression and preserve vision.
Laser photocoagulation
Focal or grid laser treatment
Targets macular edema by sealing leaking blood vessels, reducing swelling in the macula.
Panretinal photocoagulation (PRP)
Treats proliferative diabetic retinopathy by creating small burns in the peripheral retina, slowing the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
Intravitreal injections
Anti-VEGF therapy
Medications like ranibizumab (Lucentis), aflibercept (Eylea), and bevacizumab (Avastin) inhibit VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), a protein that promotes abnormal blood vessel growth. These injections reduce swelling, prevent abnormal vessel growth, and can stabilize or even improve vision.
Steroid Injections
Corticosteroids such as dexamethasone (Ozurdex) are used to reduce inflammation and fluid buildup in cases of macular edema. However, they may increase the risk of glaucoma or cataract formation.
Virectomy
For advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy involving significant vitreous bleeding or retinal detachment, a vitrectomy may be performed. This surgical procedure removes the vitreous gel, along with any blood or scar tissue, to restore vision and prevent further retinal damage.
Age-related macular degeneration (ADM)
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common eye condition and a leading cause of vision loss among older adults. It damages the macula, the central part of the retina that enables sharp, detailed vision required for activities like reading and recognizing faces. AMD occurs in two forms:
Dry AMD
Characterized by a gradual thinning of the macula and the accumulation of drusen (yellow deposits), leading to slow vision decline. Besides vitamins that have been shown to slow the disease, not much was available for dry AMD up until now. There are new medications that are now available in the US for “geographic atrophy” giving hope to these patients. This treatment is called pegcetacoplan, trade name Syfovre.
Wet AMD
Caused by the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina, resulting in fluid leakage and rapid vision loss.
Treatment options for age-related macular degeneration
While there is no cure for AMD, several treatment options can help manage the condition and slow its progression.
Anti-VEGF injections
Medications such as ranibizumab (Lucentis) and aflibercept (Eylea) are used to treat wet AMD by inhibiting abnormal blood vessel growth and reducing fluid leakage.
Lifestyle adjustments
A healthy diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can support retinal health and reduce risk factors.
Low Vision Aids
Devices like magnifiers and special glasses can help patients with advanced AMD maintain independence in daily activities.
Vitreous and retinal tears detachments
As we age, the vitreous gel inside the eye can shrink and separate from the retina, a condition known as the posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). While PVD is common and often harmless, it can occasionally lead to retinal tears or detachment.
Retinal tears
Occur when the vitreous pulls too strongly on the retina, causing a small tear.
Retinal detachments
A more serious condition where the retina separates from the underlying tissue, disrupting vision and requiring immediate treatment to prevent permanent vision loss. This can occur if retinal tears are left untreated, which is why it is important to consult quickly during signs of PVD.
Treatment options for vitreous and retinal tears detachments
The management of vitreous detachments, retinal tears, and retinal detachments depends on the severity of the condition.
Laser Surgery
A laser is used to seal retinal tears and prevent them from progressing to detachment.
Cryotherapy
Freezing therapy is applied to stabilize retinal tears and secure the retina in place.
Pneumatic retinopexy
For less severe retinal detachments, this hospital-based in-office procedure involves sealing the tear using cryotherapy or laser and injecting a gas bubble to facilitate reattachment of the retina. However, not all detachments are suitable for this approach.
Vitrectomy
For more severe retinal detachments, this surgical procedure removes the vitreous gel, repairs the retina, and restores its attachment to the underlying tissue.
Scleral buckle
Although less common, this procedure works very well and basically encircles the eye with a plastic buckle to reduce tension on the retina and reattach it, along with laser applications.
Epiretinal membranes and macular holes
An epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a thin, fibrous layer of scar tissue that forms on the surface of the retina. It can lead to vision distortion, blurriness, or difficulty focusing on fine details. A macular hole, on the other hand, is a small opening in the macula—the part of the retina responsible for central vision—causing a central blind spot or blurry vision. Both conditions primarily affect the macula and can significantly impact daily activities like reading or driving.
Treatment options for epiretinal membranes and macular holes
When symptoms become severe or vision is significantly impaired, surgical intervention is often recommended.
Vitrectomy for Epiretinal Membranes
This procedure involves removing the scar tissue from the surface of the retina to improve or stabilize vision.
Vitrectomy for Macular Holes
During this surgery, the macular hole is repaired, often by inserting a gas bubble to help close the hole and support healing.
TOP CHOICE FOR SPECIALIZED EYE CARE
Why choose Haute Vision
for retinal disease treatment
Specialized expertise in retinal diseases
Our specialists are experts in managing a wide range of retinal conditions, including diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, retinal detachment, and more. Their extensive experience ensures the best possible outcomes for every patient.
Advanced diagnostic and treatment technology
We use cutting-edge diagnostic tools and innovative treatment techniques, such as anti-VEGF therapy, laser surgery, and vitrectomy, to provide effective and precise care tailored to each patient’s unique condition.
Personalized treatment plans
Every patient receives a customized care plan based on their specific retinal condition and lifestyle needs. From managing chronic conditions to performing complex surgeries, our goal is to protect and enhance your vision. Ask about our app which has a page dedicated to reminding you of your next injection appointment.
Comprehensive follow-up care
Our commitment to your vision doesn’t end with treatment. We provide ongoing monitoring and follow-up care to track progress, manage any complications, and ensure long-term success.
